Page Not Found
Page not found. Your pixels are in another canvas.
A list of all the posts and pages found on the site. For you robots out there is an XML version available for digesting as well.
Page not found. Your pixels are in another canvas.
This is a page not in th emain menu
Published:
This post will show up by default. To disable scheduling of future posts, edit config.yml and set future: false.
Published:
This is a sample blog post. Lorem ipsum I can’t remember the rest of lorem ipsum and don’t have an internet connection right now. Testing testing testing this blog post. Blog posts are cool.
Published:
This is a sample blog post. Lorem ipsum I can’t remember the rest of lorem ipsum and don’t have an internet connection right now. Testing testing testing this blog post. Blog posts are cool.
Published:
This is a sample blog post. Lorem ipsum I can’t remember the rest of lorem ipsum and don’t have an internet connection right now. Testing testing testing this blog post. Blog posts are cool.
Published:
This is a sample blog post. Lorem ipsum I can’t remember the rest of lorem ipsum and don’t have an internet connection right now. Testing testing testing this blog post. Blog posts are cool.
ICME is one of the flagship conferences in multimedia. In this competition, participants are asked to predict whether a user will finish and like a specific short video along with its multi-modal features. My solution is ranked $3^{rd}$ out of 1028 teams from all over the world. See competition LeaderBoard.
WSDM is one of the premier conferences on web-inspired research involving search and data mining. One of the task in WSDM Cup 2019 is to detect the fake news. Given the title of a fake news article A and the title of a coming news article B, participants are asked to classify B into one of the three categories. My method is ranked 6/8 (public/private) among 94 teams from all over the world. See Kaggle competition.
The project aims at designing search algorithms to retrieval personal photos given text query. The work has been published in CLEF 2018 with title Visual Concept Selection with Textual Knowledge for Understanding Activities of Daily Living and Life Moment Retrieval. For the details of the project, please refer to the official pages.
In this task, we have to plot bounding boxes for each disease finding in a single chest X-ray without goundtruth (X, Y, width, height) in training set. The task description is detailed in PDF1 and PDF2. Our work flow could be summarized as 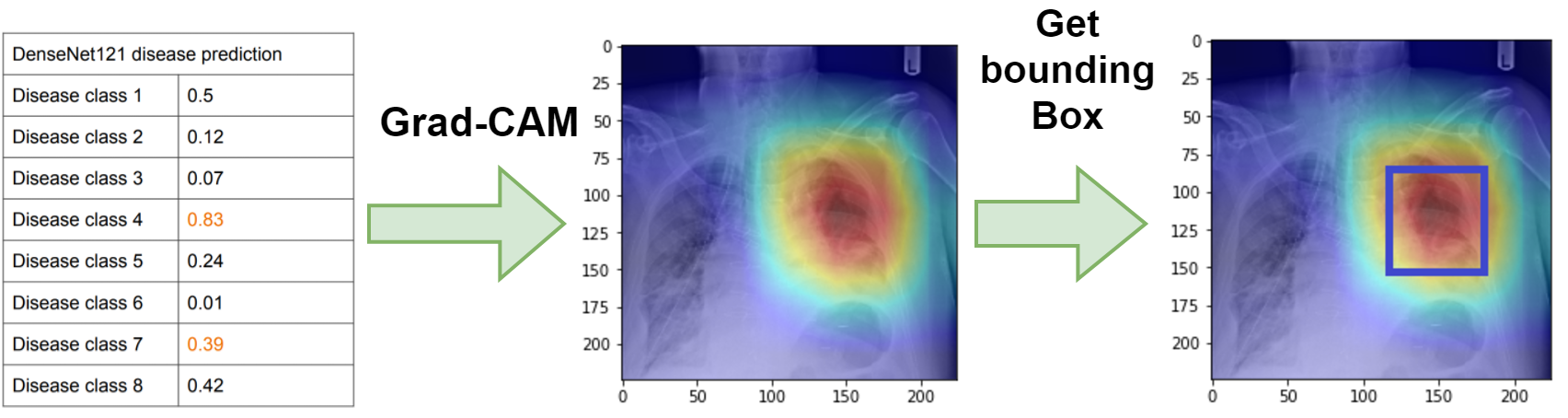
Cross-domain image retrieval is a challenging problem due to the data variations between the real-world images and advertisement images. In this work, we consider four state-of-the-art deep learning based model to extract the high-level features combining with four feature pooling strategies. Different from previous works, we further investigate the possibility of integrating the classical feature descriptors. A dataset containing half a million images of beauty and care products (Perfect-500k) is utilized for our experiments. The experimental results prove that our proposed hybrid framework can improve the mAP@7 between 3% and 10% in contrast with retrieval methods only utilizing deep features. Product pictures from different domains are show in (a) and (b) below.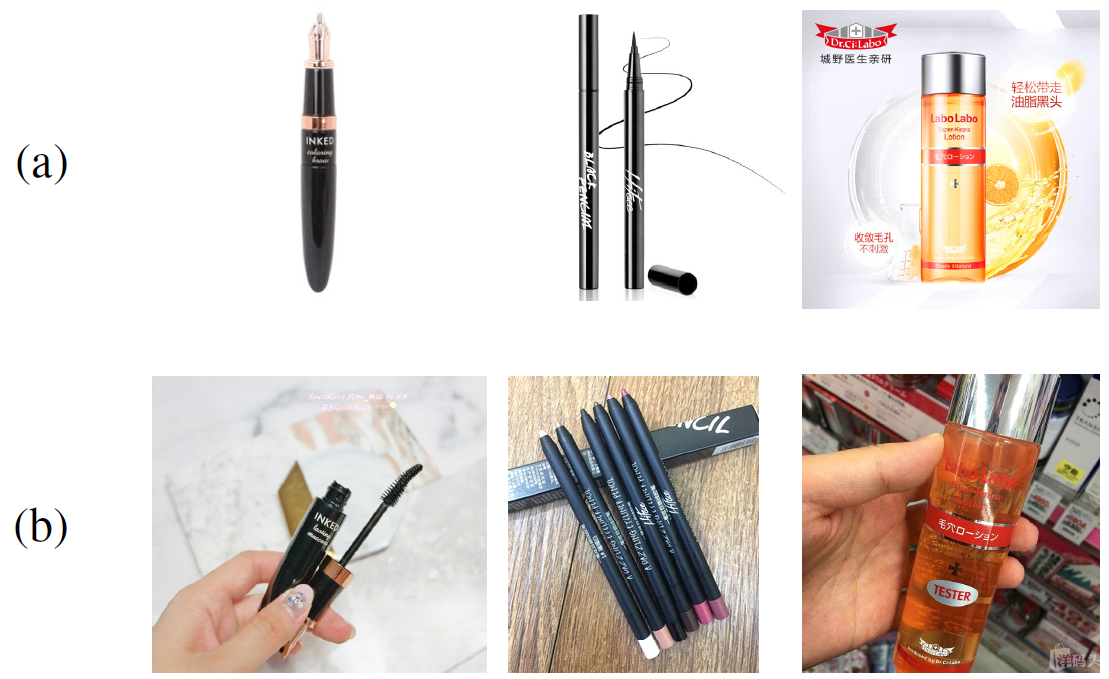 
Taiwan is considered as a small island comparing to her population. Besides, with high population density in the city area such as in Taipei city, New Taipei city, it is quite difficult to find an available parking space in those places. Therefore, we want to propose a mobile application that can provide parking lot information to customer with value-added services such as the availability of the parking lot and information about how long the customer needs to wait if the parking lot is full. With our proposed mobile application, the customer can plan their schedule in advance which can increase their satisfaction in using the facility. Moreover, with the forecasting approximate waiting time, the customer will be prepared for waiting which can help lower their frustration. Additionally, the parking lot company can better manage their parking lots via the user log in the mobile application. 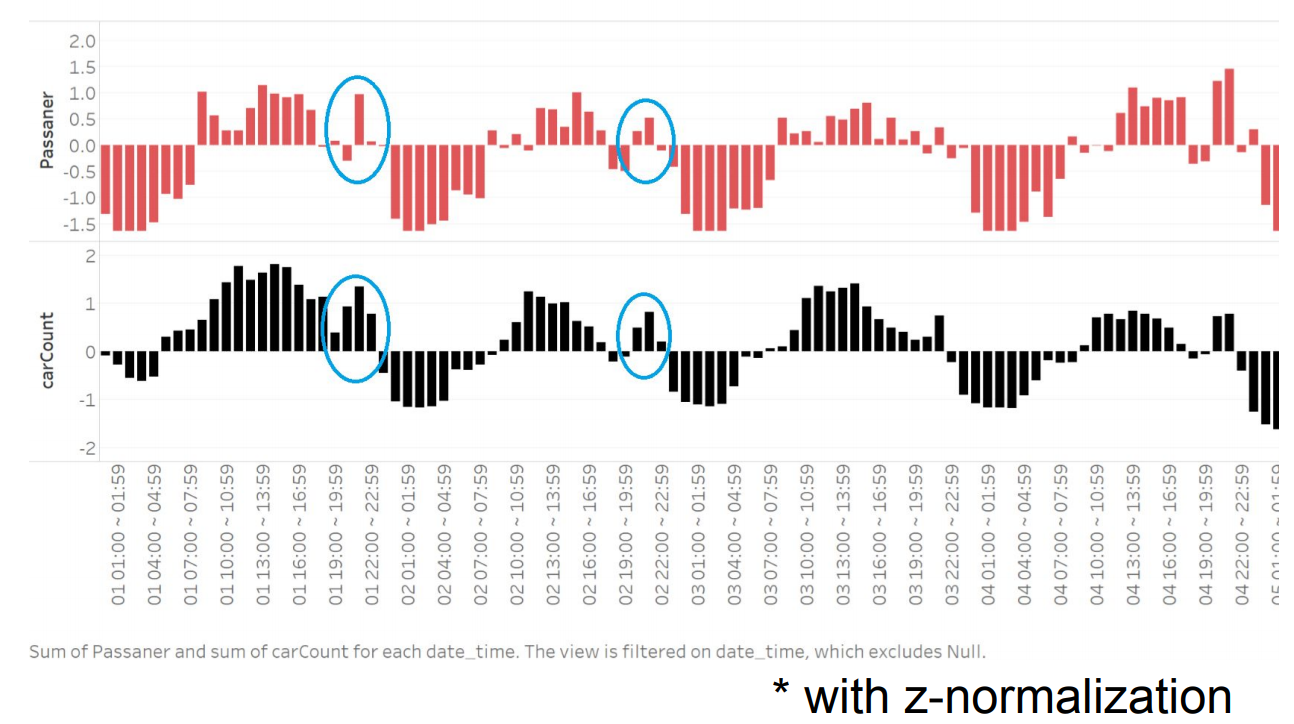
Published in CLEF, 2018
This paper presents our approach to the task of ImageCLEFlifelog 2018. Two subtasks, activities of daily living understanding (ADLT) and life moment retrieval (LMRT) are addressed. We attempt to reduce the user involvement during the retrieval stage by using natural language processing technologies. The two subtasks are conducted with dedicated pipelines, while similar methodology is shared. We first obtain visual concepts from the images with a wide range of computer vision tools and propose a concept selection method to prune the noisy concepts with word embeddings in which textual knowledge is inherent. For ADLT, the retrieved images of a given topic are sorted by time, and the frequency and duration are further calculated. For LMRT, the retrieval is based on the ranking of similarity between image concepts and user queries. In terms of the performance, our systems achieve 47.87% of percentage dissimilarity in ADLT and 39.5% of F1@10 in LMRT.
Recommended citation: Tsun-Hsien Tang, Min-Huan Fu, Hen-Hsen Huang, Kuan-Ta Chen and Hsin-Hsi Chen (2018). “Visual Concept Selection with Textual Knowledge for Understanding Activities of Daily Living and Life Moment Retrieval.” In Working Notes of Conference and Labs of the Evaluation Forum (CLEF 2018), Avignon, France, 10-14 September 2018. http://ceur-ws.org/Vol-2125/paper_124.pdf
Published in IEEE ICME Grand Challenge, 2019
Short video app, like TikTok, has received wide acclaim due to the prevalence of social media and the availability of recording devices such as mobile phones. Moreover, with the advent of the big data age, the use of historical user behaviors from multi-modal resources plays a pivotal role in the video recommendation system. In the ICME 2019 Short Video Understanding Challenge, participants are asked to predict whether a user will finish and like a specific short video along with its multi-modal features, i.e., the problem is formulated as a click-through rate prediction task. In this paper, we present an ensemble of unconventional models to the task, including tailored neural networks structure based on Compressed Interaction Network (CIN) and Gradient Boosting Decision Trees (GDBTs) using classic SVD-based features. We achieved a weighted AUC score of 0.8029 and 0.8037 on the Public and Private Leaderboard of track2, respectively, and ended up with the 3$^{rd}$ place in the competition.
Recommended citation: Tsun-Hsien Tang, Kuan-Ta Chen and Hsin-Hsi Chen (2019). “Truncated SVD-based Feature Engineering for Short Video Understanding and Recommendation.” In Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo 2019, Short Video Understanding Challenge, July 8-12, 2019, Shanghai, China. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8794898
Published in ACM WSDM, 2021
This paper demonstrates FinSense, a system that improves the working efficiency of financial information processing. Given the draft of a financial news story, FinSense extracts the explicit-mentioned stocks and further infers the implicit stocks, providing insightful information for decision making. We propose a novel graph convolutional network model that performs implicit financial instrument inference toward the in-domain data. In addition, FinSense generates candidate headlines for the draft, reducing a significant amount of time in journalism production. The proposed system also provides assistance to investors to sort out the information in the financial news articles.
Recommended citation: Yi-Ting Liou, Chung-Chi Chen, Tsun-Hsien Tang, Hen-Hsen Huang, and Hsin-Hsi Chen. 2021. FinSense: An Assistant System for Financial Journalists and Investors. In Proceedings of the 14th ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining (WSDM 2021). https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3437963.3441704
Published in ACM SIGIR, 2021
Previous studies on the financial news focus mainly on the news articles explicitly mentioning the target financial instruments, and may suffer from data sparsity. As taking into consideration other related news, e.g., sector-related news, is a crucial part of real-world decision-making, we explore the use of news without explicit target mentions to enrich the information for the prediction model. We develop a neural network framework that jointly learns with a news selection mechanism to extract implicit information from the chaotic daily news pool. Our proposed model, called the news distilling network (NDN), takes advantage of neural representation learning and collaborative filtering to capture the relationship between stocks and news. With NDN, we learn latent stock and news representations to facilitate similarity measurements, and apply a gating mechanism to prevent noisy news representations from flowing to a higher level encoding stage, which encodes the selected news representation of each day. Extensive experiments on real-world stock market data demonstrate the effectiveness of our framework and show improvements over previous techniques.
Recommended citation: Tsun-Hsien Tang, Chung-Chi Chen, Hen-Hsen Huang, and Hsin-Hsi Chen. 2021. Retrieving Implicit Information for Stock Movement Prediction. In Proceedings of the 44th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval (SIGIR 2021). https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3404835.3462999
Published:
This is a description of your talk, which is a markdown files that can be all markdown-ified like any other post. Yay markdown!
Published:
This is a description of your conference proceedings talk, note the different field in type. You can put anything in this field.
Graduate course, National Taiwan University, Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering, 2019